Springに基づくファイルアップロード
このセクションでは、HTTPマルチパートファイルを受け入れるサービスを作成します。
ファイルを受信するバックグラウンドサービスと、ファイルをアップロードするフロントページを設定します。
サーブレットコンテナを使用してファイルをアップロードするには、MultipartConfigElementクラスを登録する必要があります。以前は、web.xmlに<multipart-config>を設定する必要がありました。
そしてここで、SpringBootのおかげで、すべてが自動的に設定されます。
1.新しいファイルアップロードコントローラを作成します。
このアプリケーションには、すでにファイルを格納し、ディスクからファイルをロードするためのクラスがいくつか含まれています。これらはcn.tiny77.guide05パッケージに含まれています。 これらのクラスはFileUploadControllerで使用します。
package cn.tiny77.guide05;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.MvcUriComponentsBuilder;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.RedirectAttributes;
@Controller
public class FileUploadController {
private final StorageService storageService;
@Autowired
public FileUploadController(StorageService storageService) {
this.storageService = storageService;
}
@GetMapping("/")
public String listUploadedFiles(Model model) throws IOException {
List<String> paths = storageService.loadAll().map(
path -> MvcUriComponentsBuilder.fromMethodName(FileUploadController.class,
"serveFile", path.getFileName().toString()).build().toString())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
model.addAttribute("files", paths);
return "uploadForm";
}
@GetMapping("/files/{filename:.+}")
@ResponseBody
public ResponseEntity<Resource> serveFile(@PathVariable String filename) {
Resource file = storageService.loadAsResource(filename);
return ResponseEntity.ok().header(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION,
"attachment; filename="" + file.getFilename() + """).body(file);
}
@PostMapping("/")
public String handleFileUpload(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file,
RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) {
storageService.store(file);
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("message",
"You successfully uploaded " + file.getOriginalFilename() + "!");
return "redirect:/";
}
@ExceptionHandler(StorageFileNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> handleStorageFileNotFound(StorageFileNotFoundException exc) {
return ResponseEntity.notFound().build();
}
}
SpringMvcはそれに基づいて適切なルートを設定できるように、クラスには@Controllerというアノテーションが付けられています。 各@GetMappingアノテーションと@PostMappingアノテーションは、対応するリクエストパラメータとリクエストタイプを特定のメソッドにバインドします。
GET / StorageServiceを介してファイルリストをスキャンし、Thymeleafテンプレートにロードします。 MvcUriComponentsBuilderを使用してリソースファイルの接続アドレスを生成します。
GET / files / {filename}ファイルが存在する場合、ファイルを読み込んでブラウザに送信します。 ファイルは、 "Content-Disposition"ヘッダーを設定することによってダウンロードされます。
POST /マルチパートファイルを受け入れ、Storage Serviceに保存します。
コントローラがストレージレイヤを操作するのに役立つサービスインタフェースStorageServiceを提供する必要があります。 インターフェースはおおよそ以下の通りです
package cn.tiny77.guide05;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public interface StorageService {
void init();
void store(MultipartFile file);
Stream<Path> loadAll();
Path load(String filename);
Resource loadAsResource(String filename);
void deleteAll();
}
以下は、インタフェース実装クラスです
package cn.tiny77.guide05;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardCopyOption;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.UrlResource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.FileSystemUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
@Service
public class FileSystemStorageService implements StorageService {
private final Path rootLocation;
@Autowired
public FileSystemStorageService(StorageProperties properties) {
this.rootLocation = Paths.get(properties.getLocation());
}
@Override
public void store(MultipartFile file) {
String filename = StringUtils.cleanPath(file.getOriginalFilename());
try {
if (file.isEmpty()) {
throw new StorageException("无法保存空文件 " + filename);
}
if (filename.contains("..")) {
// This is a security check
throw new StorageException(
"无权访问该位置 "
+ filename);
}
Files.copy(file.getInputStream(), this.rootLocation.resolve(filename),
StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);
}
catch (IOException e) {
throw new StorageException("无法保存文件 " + filename, e);
}
}
@Override
public Stream<Path> loadAll() {
try {
return Files.walk(this.rootLocation, 1)
.filter(path -> !path.equals(this.rootLocation))
.map(path -> this.rootLocation.relativize(path));
}
catch (IOException e) {
throw new StorageException("读取文件异常", e);
}
}
@Override
public Path load(String filename) {
return rootLocation.resolve(filename);
}
@Override
public Resource loadAsResource(String filename) {
try {
Path file = load(filename);
Resource resource = new UrlResource(file.toUri());
if (resource.exists() || resource.isReadable()) {
return resource;
}
else {
throw new StorageFileNotFoundException(
"无法读取文件: " + filename);
}
}
catch (MalformedURLException e) {
throw new StorageFileNotFoundException("无法读取文件: " + filename, e);
}
}
@Override
public void deleteAll() {
FileSystemUtils.deleteRecursively(rootLocation.toFile());
}
@Override
public void init() {
try {
Files.createDirectories(rootLocation);
}
catch (IOException e) {
throw new StorageException("初始化存储空间出错", e);
}
}
}
2、Htmlページを作成する
ここでThymeleafテンプレートを使用する
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<body>
<div th:if="${message}">
<h2 th:text="${message}"/>
</div>
<div>
<form method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data" action="/">
<table>
<tr><td>File to upload:</td><td><input type="file" name="file" /></td></tr>
<tr><td></td><td><input type="submit" value="Upload" /></td></tr>
</table>
</form>
</div>
<div>
<ul>
<li th:each="file : ${files}">
<a th:href="${file}" rel="external nofollow" th:text="${file}" />
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
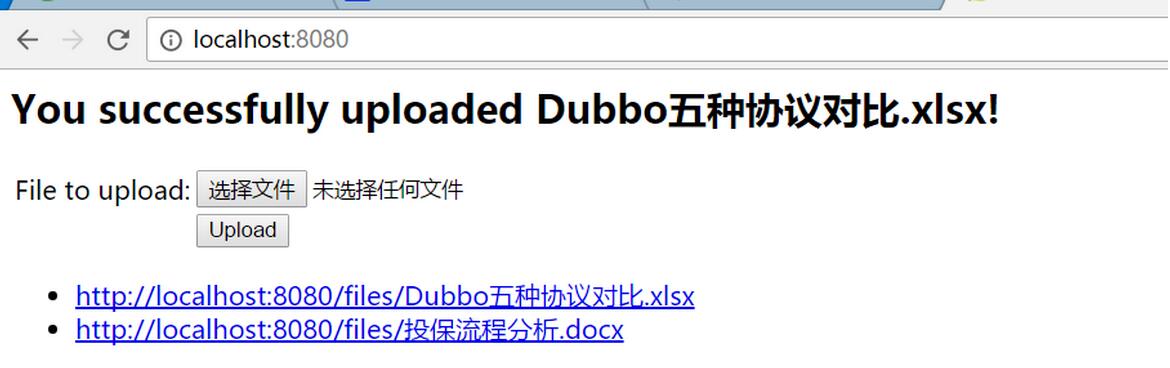
ページは主に3つの部分に分かれています。
– 上にはSpringMvcが渡した情報が表示されます
– ユーザーがアップロードしたファイルを提供するフォーム
– バックグラウンドで提供されるファイルのリスト
3、アップロードされたファイルのサイズを制限する
ファイルアップロードアプリケーションでは、通常、ファイルサイズを設定する必要があります。スプールされたファイルが5 GBの場合、どれくらいの悪さがあるとしますか? SpringBootでは、プロパティファイルを制御できます。
新しいapplication.propertiesを作成すると、コードは次のようになります。
Spring.http.multipart.max-file-size = 128KB#合計ファイルサイズは128kbを超えることはできません
Spring.http.multipart.max-request-size = 128KB#要求されたデータサイズは128kbを超えることはできません
4、アプリケーション開始機能
package cn.tiny77.guide05;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties(StorageProperties.class)
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
CommandLineRunner init(StorageService storageService) {
return (args) -> {
storageService.deleteAll();
storageService.init();
};
}
}
図5に示すように、